Engineering information
Efficiency improvement calculation
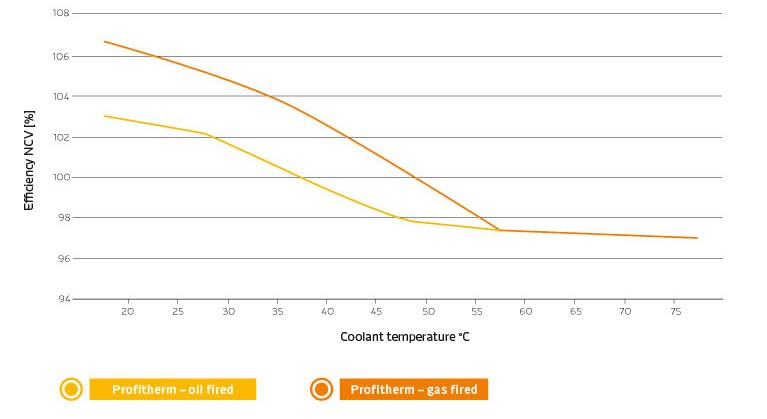
In condensing and flue gas heat recovery systems, the water-side temperature level at which the heat exchanger is operated is decisive for efficiency.
The colder the return (coolant mass flow), the better the energy yield and the better the heat exchanger self-cleaning effect that occurs as a result of condensation.
Design of AWR pump
- The mass flow rate required to cool the flue gas heat exchanger is calculated for a temperature differential between the heat exchanger inlet and outlet of 5–10 K (standard applications).
- The water-side pressure drop of the heat exchanger can be found in the relevant datasheets.
- The output of the flue gas heat exchanger can be found from the efficiency improvement of the system; see diagram below.
- The required minimum water volume of the heat exchanger should be borne in mind when selecting the pump.
Example
A 100 kW boiler system has a combustion efficiency without BOMAT heat exchanger of about 91 %.
With a BOMAT heat exchanger the efficiency increases to 101 %.
The heat exchanger output is 100 kW x 10 % = 10 kW.
For a temperature differential between the heat exchanger flow and return of 10 K, the AWR pump must provide a mass flow rate of 861 kg/h.
We are happy to provide an individual quote for your project. To request a quotation, please complete our form.